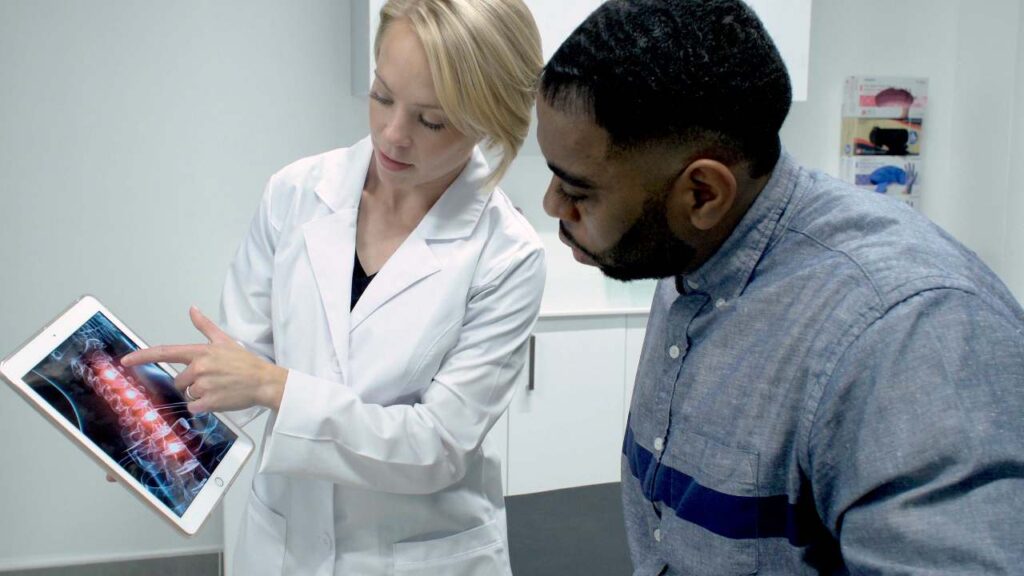
Varicose veins or venous reflux occurs when unidirectional valves in the veins don’t close properly and blood starts to travel backwards. Veins start to dilate the channels that otherwise would not be visible forming tortuous and enlarged superficial veins among other symptoms and signs. The regions of the lower extremities that are commonly affected with varicose veins are the thighs, calves, ankles, and feet. Venous reflux can also be the cause of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) as well as Superficial Thrombophlebitis (SVT) which can originate occlusive blockage of blood or non occlusive blockage. When there is presence of a blood clot, pain, swelling, and redness will occur. Patients would try to avoid movement because of the discomfort this situation causes.
In cases that are very serious, a blood clot can cause a pulmonary embolism because the clot can disconnect. It then travels in the bloodstream to the heart and lungs. When this happens, it is considered an emergency situation and rapid response is advised to prevent death. There are symptoms that can help us identify the presence of a DVT or blood clot such as:
Leg pain: leg pain can occur when a blood clot is present even when we are not moving; but pain can increase when you are walking, standing, or going up and down stairs.
Leg Swelling: leg swelling is another symptom of a blood clots. Swelling can be prominent in the area affected with a clot. Some examples are the thigh area, behind the knee area, proximal, mid, or distal calf area, and ankle area and foot.
Leg fatigue: Leg fatigue is very common with the presence of a blood clot because leg feels heavy when moving around and therefore it is painful and tiring to change position.
Increased temperature: Area affected with a clot can be warm or hot to the touch as well as reddish and swollen with discoloration in the different areas that are affected.
Dilated painful veins: For superficial veins that becomes clotted, a cord like visible dilated vein in the surface of the skin is painful to the touch, swollen, and visible.
Pulmonary embolism symptoms: If a blood clot is dislodged and travels to the lungs, it can cause symptoms that are considered severe, serious, and should be treated with emergency. Some of the symptoms are chest pain, chest pressure, increased heart rate, dizziness, vomiting, and coughing with blood.
Situations in life can get together to cause a DVT ( Deep vein thrombosis) or Superficial Thrombophlebitis (SVT). Many times if we become aware of this situations we can help to prevent what can be avoided such as:
Moving around avoiding immobility: In times when we sit for long periods of time like in a long car ride or air flight, frequent stops are recommended or walking around each hour for 10 minutes. In case where immobility is unavoidable, then the use of other methods like medical compression hoses or certain exercises involving flexion of the muscles or physical therapy must be done to improve circulation and diminish blood stasis.
Controlling body weight with aging: A healthy life style and diet is recommended to control excess weight which could cause extra pressure in the lower abdomen and lower extremities increasing this way the risk for venous disease and thrombus formation, specially as we get older or other risk factor also contribute.
Health Habits: Avoiding harmful choices like smoking is beneficial to circulation and helps to prevent health complications related to Chronic Pulmonary Obstructive Disease (COPD) in relation to Venous Disease, Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), and Pulmonary Embolism (PE). Do not smoke, this will help to prevent immobility and hyper coagulability because of COPD and at the same time you will prevent risk of venous thromboembolism and venous disease.
Pregnancy and Conservative Management: Pregnancy and the extra weight in women can also be a risk to develop venous disease, clots, and varicose veins. Be aware that there are conservative managements that can be implemented during pregnancy to manage the extra weight and venous stasis. There are also minimally invasive procedures to manage varicose veins after pregnancy offered by vein experts in Venous Disease. A vein specialist can help you get in control with the use of medical compression stockings, exercises, position management, and if necessary advanced vein treatments.
Trauma and Operative Procedures: In times when bedrest cannot be prevented, there is risk for Venous Thromboembolism (VT) and the way it can be prevented is by taking medication that makes the blood thiner and wearing medical compression hoses.
Genetically Predisposed: Medical management is recommended if there is family history of disorders or a genetic condition that puts you at risk to develop venous thromboembolism or venous disease.